VERNACULAR ARCHITECTURE
|
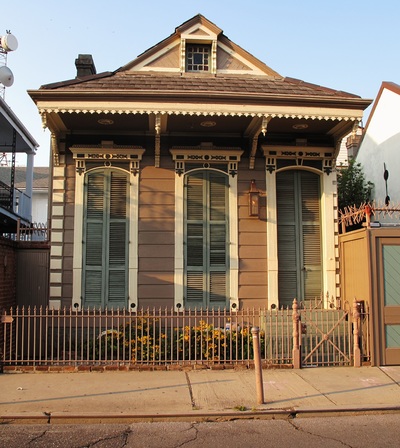
The image on the left is a typical shotgun house. The middle image is a camel back shotgun house, and the image on the right is a double shotgun house.
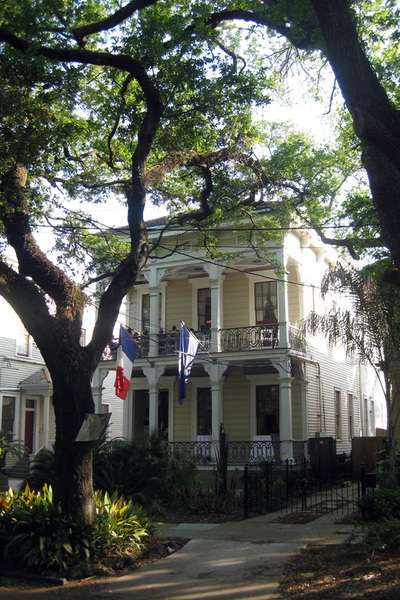
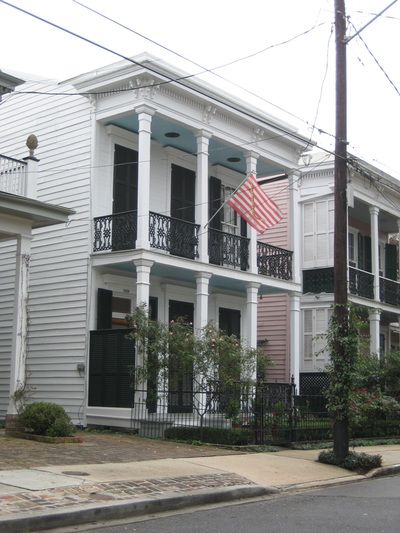
The image on the left is a row of creole style townhomes, and the image on right is a double gallery townhouse.
This is a picture of an old creole cottage.
Architectural Styles
|
SHOTGUN HOUSE
The shotgun house is one of the most common types of homes for the middle and lower classes in New Orleans. This type of house is one room wide and three to five rooms deep. The shotgun house usually has a porch with a symmetrical facade and shuttered windows and doors. There are many variation of the typical shotgun house. One of those variations is the camel back shotgun. Unlike the typical one story shotgun house these houses have a second story addition on the rear of the home. Another variation of the classic shotgun house is the double shotgun. This house is a two residence home, 2 rooms wide and 3-5 rooms deep. The facade is the same as the classic shotgun house but it is reflected and has an overhanging roof. TOWNHOUSE The townhouse is a very tall and narrow house. This house would most be seen in areas like the French Quarter. The houses are 2-3 stories tall and very long. The townhouse has a long, narrow footprint oriented to the street. There is a grand entrance door leading into a hallway that passes by the rooms. There also distinct styles of townhomes. One of the main styles is the Creole townhouse. This is a lot like a two story creole cottage, it has a symmetrical facade, and dormers on the roof. There are balconies that open up to the street, and a distinct creole style. Another type of townhouse is the American townhouse. This style has an extravagant facade leading into a main entrance with a hallway. The last style is the double gallery style. This style, like the American townhouse, has an extravagant facade. Unlike the American townhouse the double townhouse is twice as wide and goes straight back like a shotgun house. There are many other styles of townhomes that vary with time and style, but they are all similar to these three. CREOLE COTTAGE One of the first styles of vernacular architecture was the creole cottage. This design was heavily influenced by both French and Spanish construction methods and the local climate. The typical Creole Cottage is 1‐ to 1½‐ stories tall, 2 rooms wide and 2 rooms deep, often with small storage rooms. These houses were very simple in design but still functional. Creole Cottages have hipped or side gabled roofs, frequently with tall, narrow dormer windows. The cottages have an overhang over the front of the building to protect from weather and 4 symmetrical openings in the front of the building. CREOLE The creole style is a very distinct style that originated in New Orleans. Creole is a blend of the French, Spanish, and Caribbean architectural influences fused with the demands of the hot and humid climate. Some elements of the creole style are brick, stucco, french doors, no dominate entrances, and shutters. The creole style was also very simplistic and wasn’t blended with other styles. These design principles can be found in architecture around the city. GREEK REVIVAL This style of design is very prevalent in the design of the southern homes like the ones in New Orleans. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the architecture of the Greek world was brought back because it was a symbol of democracy. Some key elements of the Greek revival style that are present in the vernacular design in New Orleans include trim around windows and doors, and full height porches with round columns or boxed piers. Also roofs are topped with triangular designs, and are gabled or hipped. The Greek revival design was primarily shown in mansions and plantation homes, but it showed up a lot in townhouses and shotgun homes. ITALIANATE
Was a style during the 19th century which was influenced by early Italian Renaissance and Northern Italian vernacular architecture.It was first popular in England and the American East Coast which began in the 1840's and came to New Orleans in in the 1850's. Some characteristics about this style are windows that can be tall,double hung,four over four,two over two or two over one, with arched heads and hood moldings that are symmetrical facades with hipped roofs. This style can be seen all over different houses but mostly on shotgun houses. QUEEN ANNE/ EASTLAKE
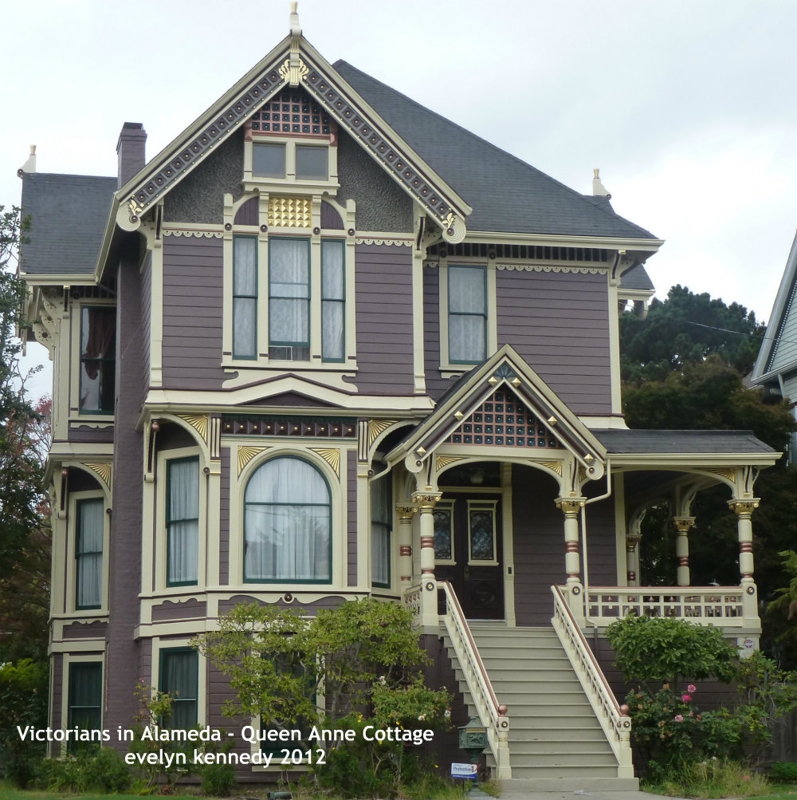
The Queen Anne and Eastlake styles came in to New Orleans in the 1870s and continued to be used up until the early 20th century. The styles were widely popular across the US, spread through the use of commonly available architectural pattern books and made possible by new mechanized woodworking techniques. Elements of both styles are similar and often intermixed. ECLECTIC/EXOTIC REVIVALS
A variety of homes were built whose design drew inspiration from popular conceptions of Italian villas, Renaissance palaces, medieval English cottages, Gothic Revival church buildings, Spanish Mission architecture and many other picturesque architectural styles-https://www.nola.gov/nola/media/HDLC/Guidelines/03-TypesStyles.pdf
This style can be found in New Orleans which basically was a style that turns things from normal to something from the past influenced by Spanish architecture. |
CULTURE OF NEW ORLEANSNew Orleans as a whole seems completely unusual to the average American, as the cultural diversity of the city has no limits. It combines traits of both northern and southern U.S. cities, as well as the cultural aspects of the Native Americans and European settlers. Most people that visit the city can find a handful of things relatable and recognizable from their hometown, but a good majority of things found in the city would seem completely out of place. Most American people would find New Orleans unusual, but that is because it truly is not like any other city in the U.S., as it seems to be more like a European city than an American one.
|
|
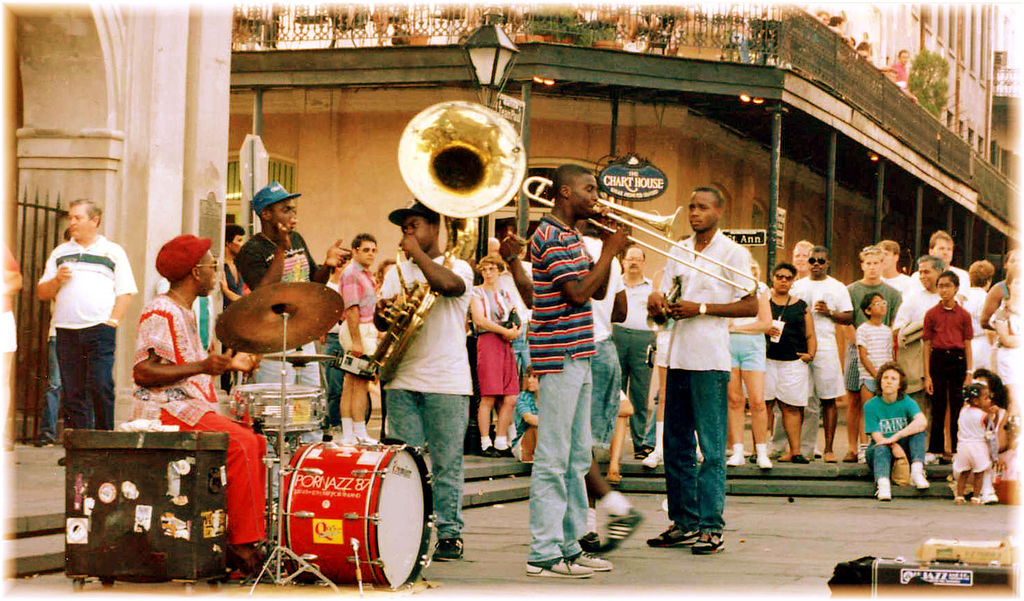
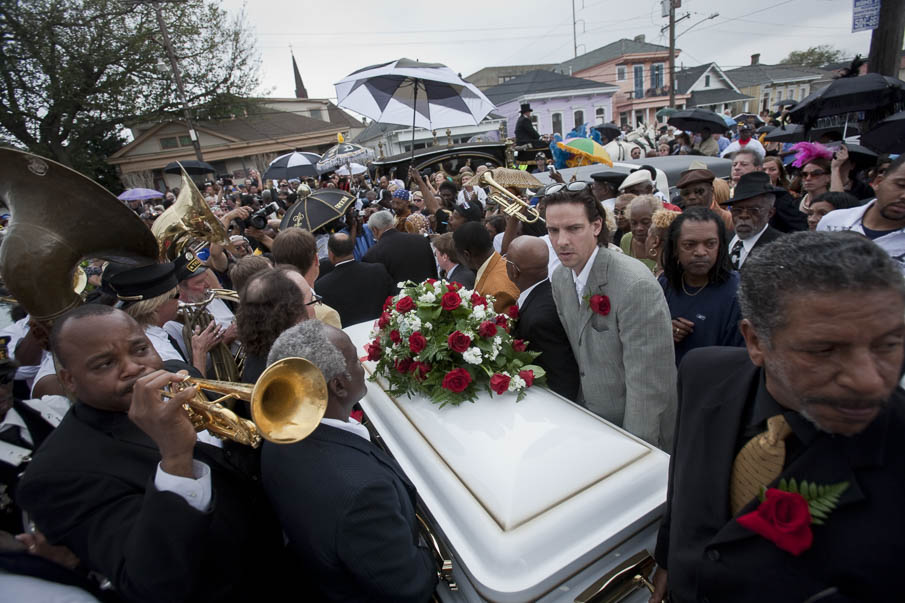
The culture of New Orleans is usually different columns like music, art, movies, Broadway, and etc. the topic music the type of music that people play and make is Jazz and they always play Jazz in funerals in celebration and all other events. another topic is food or what I mean is recipes the well know dish in new Orleans is Gumbo is a type of beef stew and every recipes is different pass down generations to generations another thing they like they like to cook seafood shellfish. the last thing is sports the NFL is the new Orleans saints to me the saints is one of the best team in the NFL.
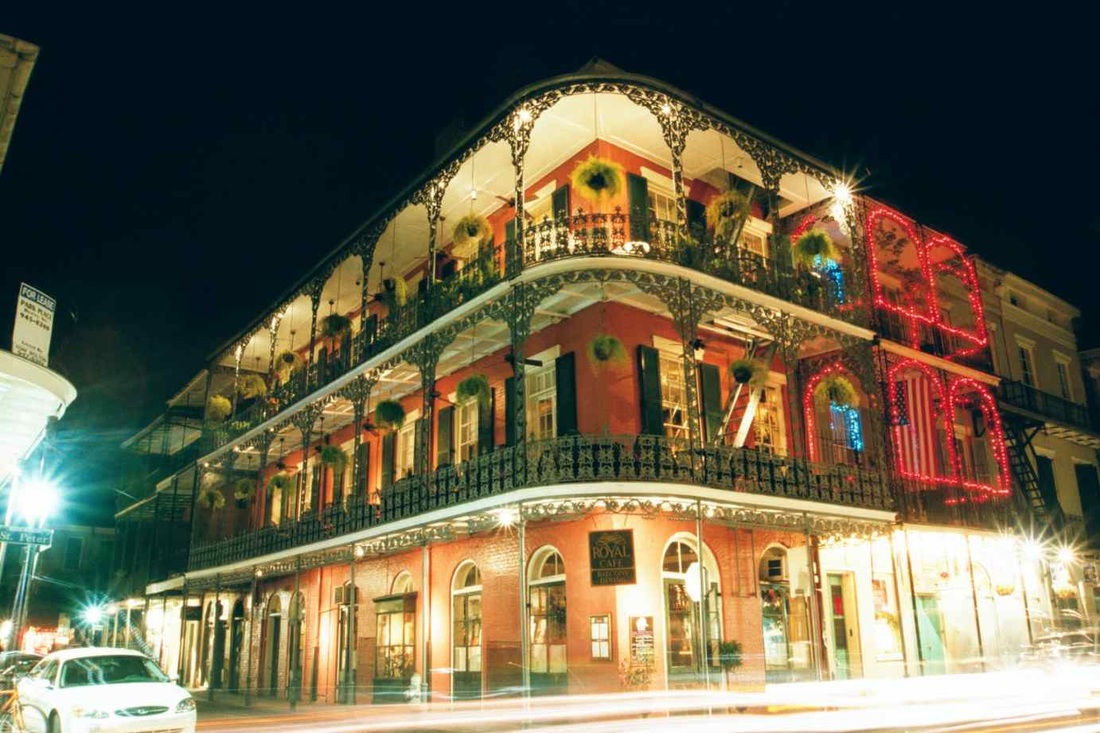
The French Quarter-The French Quarter is one of the most unique parts of New Orleans, as it is authentically French, not a reproduction of French culture.
-The French Quarter had great luck during hurricane Katrina, as it was not completely destroyed, Conserving a great treasure of the New Orleans culture. -The French Quarter was founded by, and possessed by the French originally but was taken by the Spanish. During the Spanish rule, Two devastating fires occurred, allowing the Spanish to rebuild in their own style, resulting in a great contribution to the vast mix of architecture today. |
A Cultural Melting Pot
|
Throughout history, many different groups of different ethnicities and from different cultures passed through New Orleans, leaving their cultural mark on the city.
Cultural Influences on New Orleans: In New Orleans, there is a mix of multiple cultures including: African American, Creole, French, German, Irish, Italian, Jewish, Spanish, and Vietnamese -was considered a getaway for people from Europe and Africa to go and explore more about the different cultures n new Orleans -before was a slave trade area with ships -most people are religious in the area -New Orleans is a foreign place and more european than american. -Have a vibrant urban folk culture -many neighborhood restaurant open by creative chefs http://gatewayno.com/history/histroy.html http://www.latech.edu/tech/liberal-arts/geography/courses/310/text/french.htm http://www.neworleansonline.com/neworleans/multicultural/multiculturalhistory/ |
|