culture in SYRIA
R E L I G I O N:
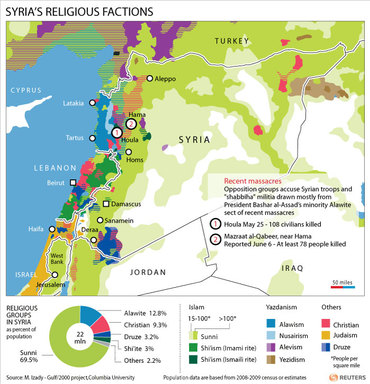
Most of the Syrian population (80%) is Arab but differences in religion are tolerated as there are religious minorities such as Druze, Christianity, and different Muslim sects. Each minority largely identifies with their religion hence creating geographical and cultural sects. Palestinian Refugees also became a minority after fleeing to Syria in 1948.
Most of the Syrian population (80%) is Arab but differences in religion are tolerated as there are religious minorities such as Druze, Christianity, and different Muslim sects. Each minority largely identifies with their religion hence creating geographical and cultural sects. Palestinian Refugees also became a minority after fleeing to Syria in 1948.
H I S T O R Y:
Syria used to be apart of Jordan, Israel, and Lebanon known as an area called Sham. The country was well known for it's coastal kingdoms and convenient trading posts. Conquered by the Persians, Greeks, Romans, and eventually the Muslim Arabs, Syria has had many influences. Eventually taken over by the Turkish Ottomans until their fall and then by the French who set up Syria's parliamentary government. Syrians weren't happy with the French so there were tensions that eventually led the French to bomb Damascus.
Syria used to be apart of Jordan, Israel, and Lebanon known as an area called Sham. The country was well known for it's coastal kingdoms and convenient trading posts. Conquered by the Persians, Greeks, Romans, and eventually the Muslim Arabs, Syria has had many influences. Eventually taken over by the Turkish Ottomans until their fall and then by the French who set up Syria's parliamentary government. Syrians weren't happy with the French so there were tensions that eventually led the French to bomb Damascus.
S O C I E T Y:
Syrian society reflects traditions passed down by their previous rulers (Persians, Ottomans, etc.) as society there is very stratified. There are social classes that are generally accepted without complaint and no interaction. Skin color also defines social class as the lighter you are, the higher positions you are able to hold. Long robes and clothing that hide most of the body except for hands and feet are typical attire for women and men; however, younger people of higher class gravitate towards Western culture.
Syrian society reflects traditions passed down by their previous rulers (Persians, Ottomans, etc.) as society there is very stratified. There are social classes that are generally accepted without complaint and no interaction. Skin color also defines social class as the lighter you are, the higher positions you are able to hold. Long robes and clothing that hide most of the body except for hands and feet are typical attire for women and men; however, younger people of higher class gravitate towards Western culture.
|
L A N G U A G E:
90% of the population speaks Arabic but Kurdish, Armenian, and Circassia are also spoken in different regions of the country. Ancient languages such as Maalua, Aramaic, and Syria are also spoken but not as much. International languages include French and English which are mostly spoken by educated individuals. |
culture in IRAQ
R E L I G I O N:
Most of the Iranian population (95%) practice Islam: however, there are two forms of Islam practiced in Iraq, Sunni and Shia in which the Shia are more prevalent in Iraq then the Sunnis. In Islam there are no distinctions between church and state as in the US. A small portion of the population does consist of Christians under the churches of Chaldean, Nestorian, Jacobite (Syrian) Orthodox, and Syrian Catholic. A religion that combines paganism, Zoroastrianism, Christianity and Islam is also practiced by a small number of people.
Most of the Iranian population (95%) practice Islam: however, there are two forms of Islam practiced in Iraq, Sunni and Shia in which the Shia are more prevalent in Iraq then the Sunnis. In Islam there are no distinctions between church and state as in the US. A small portion of the population does consist of Christians under the churches of Chaldean, Nestorian, Jacobite (Syrian) Orthodox, and Syrian Catholic. A religion that combines paganism, Zoroastrianism, Christianity and Islam is also practiced by a small number of people.
H I S T O R Y:
Iraq is under the area in which the prehistoric civilization of Mesopotamia was located. They have been under the rule of Sumerians, Babylonians, Persians, and then finally the Muslim Arabs in which the country today was most influenced by. The Arab culture is the most prevalent culture in Iraq and most Arabs in this country are Muslim.
L A N G U A G E:
Most of the population speaks Classical, Modern Standard, and Spoken Arabic. Kurdish is also spoken among the minority languages of Aramaic, Turkic, Armenian, and Persian.
Most of the population speaks Classical, Modern Standard, and Spoken Arabic. Kurdish is also spoken among the minority languages of Aramaic, Turkic, Armenian, and Persian.
economy in IRAQ
Jobs refugees and volunteers can do (generalized).
- Teaching
- Doctor/health care
- Building
- Animal care
- Youth and child care
- Environmental
- Women's care
- Elderly care
- News
- Sports
- Farming
Iraqis Jobs:
Iraqis Economic History:
The Persian gulf war caused the Iraqis to have an economic crisis. The United Kingdom's put a plan in order for them to survive. Were they trade some of their natural resources for food and medicine for their people alone. they smuggled some of that to nearby nations for money. They use to import most of their food till a food shortage. They then, had to grow most of their food, but because most of their lands can't be farmed. The nation haft to get their food through rations at the first of the month.
Syrian Economics
The land in syria is mostly desert. That means there is hardly no farming at all. They like the iraqis have mostly mining and drilling for their economic bases. Because of its dense population they have a hard time with their economy.
Refugee Life
Refugees in their camps come with nothing but the clothes on their backs and themselves. They have to find jobs or set up a shop/business. Kids learn as normal, adults get payed but a little less. The shops usually have toys, clothes, food, and candy. Power is scarce in the camps same with plumbing. Cooking is hard to do same with storing the food, so most of the foods are things you can preserve easily or eat that meal. Water is hard to get you have to walk far to get any. When you finally get money getting these items is easier.
- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kurdish_Refuge_Camp_in_Suruc_Turkey.jpg
- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Working_together_to_help_Syrian_refugee_children_in_Lebanon_(15089979007).jpg
- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:A_bakery_shop_at_Al-Zaatari_camp.jpghttp://www.everyculture.com/Ge-It/Iraq.html
- https://www.abroaderview.org/?gclid=EAIaIQobChMI_ZnLmaKO1gIVz2B-Ch06VAvTEAAYAiAAEgK8dfD_BwE
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Egyptians
economy in SYRIA
loss of culture in REFUGEE CAMPS
culture in REFUGEE CAMPS
Told by the lives that live in refugee camps, the culture is very dry in a refugee camp. Obviously is it more about survival at this point in time for these helpless people. During the uplifting moments at these hard times, these refugees do maintain some cultural activities to keep spirits up.
maptia.com/reza/stories/exile-voices
maptia.com/reza/stories/exile-voices
economy in REFUGEE CAMPS
In Jordan, the largest Syrian refugee camps in the world, were supposed to provide temporary housing when the government and United Nations opened it. But since residents have not been able to leave, they have started 3,000 businesses and cities nearby have loosened employment restrictions. Not only does having refugee camp market places provide the goods and services needed by the residents, but the market also serves as a pastime, place for community building, and source of income, dignity, ownership, and pride.
However some camps that were pre designed with shops do not prosper because the Syrian Refugee Affairs Directorate (SRAD) are hesitant in giving jobs to Syrians, hence making them reliant on humanitarian funds.
http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/worlds-largest-syrian-refugee-camp-has-developed-its-own-economy/